Table of Contents
ToggleI Introduction
In India’s rapidly expanding economy, large-scale infrastructure and industrial projects are becoming increasingly common. However, with capital-intensive initiatives come significant risks—both technical and financial. As banks and financial institutions grow more cautious in lending, due diligence has transformed from a formality into a strategic necessity. This is where Techno-Economic Viability (TEV) studies come into play.
A TEV study is a comprehensive assessment of a project’s technical feasibility and economic viability, performed before significant capital is deployed. It involves analyzing project design, technology, market potential, cost structures, and financial sustainability.
TEV consultants are professionals or specialized firms that conduct these assessments. Their role has become central to India’s project financing ecosystem. Whether it is a greenfield infrastructure project, a manufacturing expansion, or the restructuring of a distressed asset, TEV consultants help stakeholders evaluate whether a project is worth pursuing—and on what terms.
For banks, TEV consultants act as an independent filter against non-performing assets (NPAs). For project promoters, they serve as a strategic sounding board, helping them refine execution models and enhance bankability. In an environment where access to credit is both competitive and compliance-driven, TEV consultants serve as vital enablers of trust and transparency.
II. Who is a TEV Consultant?
A TEV Consultant—short for Techno-Economic Viability Consultant—is a subject matter expert or consulting firm that specializes in evaluating large projects from two key perspectives: technical feasibility and economic viability.
These consultants are typically engaged by banks, financial institutions, private equity firms, or project promoters to assess whether a proposed or ongoing project meets industry, financial, and regulatory standards. Their deliverable is the TEV report, which forms a crucial component of the decision-making process for loan sanction, investment, or restructuring.
The core objective of a TEV consultant is to ensure that the project is:
- Technically sound in terms of its engineering, technology, and operations.
- Economically viable with respect to market dynamics, pricing, competition, and demand.
- Financially robust in terms of profitability, cash flow, and return metrics.
TEV consultants are most frequently engaged in projects where:
- A large term loan is being sought from a bank or NBFC.
- The project involves imported technology or high-capital machinery.
- The promoter seeks funding from private equity or venture capital.
- There is a need for loan restructuring or stress asset resolution.
TEV consultants often work in multidisciplinary teams comprising engineers (mechanical, electrical, civil, etc.), chartered accountants, MBAs, industry experts, and market researchers to offer a 360-degree view of a project’s potential and risk profile.
III. Why TEV Consultants are Crucial in India
The importance of TEV consultants in the Indian business and finance landscape cannot be overstated. As financial institutions tighten their lending norms and regulators push for higher accountability, TEV studies have become a mandatory prerequisite for project financing in many sectors.
1. Mandatory for Large Project Funding
For capital-intensive ventures—such as infrastructure, energy, manufacturing, and real estate—banks and NBFCs often require a TEV report as a condition for sanctioning term loans or working capital limits. These reports form the foundation for risk evaluation and help institutions decide whether the project qualifies for funding, what quantum of loan to approve, and under what conditions.
2. Prevention of Non-Performing Assets (NPAs)
India’s banking sector has struggled with high levels of NPAs in the past decade. One of the root causes has been inadequate due diligence during the project appraisal stage. By evaluating both technical and economic parameters objectively, TEV consultants help filter out weak or unrealistic proposals before funds are disbursed, thereby reducing the chances of future loan defaults.
3. Promoting Financial Discipline and Bankability
TEV consultants guide project promoters in refining business plans and correcting technical assumptions. This process ensures that only bankable and technically sound projects are taken forward. It also enhances transparency between the borrower and the lender, creating a solid foundation for long-term financial engagement.
IV. Core Functions of a TEV Consultant
TEV consultants offer a combination of technical, financial, and market expertise. Their primary deliverables revolve around evaluating projects on multiple dimensions to ensure that they meet viability standards. The following are the key responsibilities they undertake:
1. Techno-Economic Viability Assessment
This is the core function of a TEV consultant. It involves a thorough analysis of the project’s:
- Technical feasibility: Assessment of technology, plant and machinery, project site, engineering design, supply chain, and operational processes.
- Economic viability: Analysis of market demand, industry trends, pricing, competition, scalability, and long-term sustainability.
2. Preparation of Detailed TEV Reports
A TEV consultant compiles all findings into a structured report, typically required by financial institutions. These reports include:
- Executive summary and promoter profile
- Technical specifications and project cost breakdown
- Financial projections: cash flows, IRR, DSCR, break-even, NPV
- SWOT analysis and risk mitigation strategies
- Recommendations for improvement or restructuring
The report is drafted in line with guidelines issued by institutions like SBI, Bank of India, and SIDBI, ensuring consistency with regulatory expectations.
3. Support to Banks, NBFCs & Investors
TEV consultants act as third-party evaluators on behalf of lending institutions. Their insights help lenders validate key project assumptions, identify hidden risks, and determine the right funding structure. For private equity or venture capital firms, TEV studies serve as a part of the investment due diligence process.
4. Mitigation of Project Risks
Early detection of red flags—such as outdated technology, supply chain disruptions, unrealistic demand forecasts, or non-compliant project designs—can help promoters pivot before irreversible decisions are made. TEV consultants provide this risk intelligence upfront, increasing the project’s chance of success.
5. Ensuring Regulatory & Policy Compliance
Many sectors in India are subject to extensive regulations—environmental clearances, land acquisition, pollution control, energy usage, etc. TEV consultants ensure that proposed projects are in alignment with applicable laws, government policies, and institutional guidelines, which is essential for both loan approval and long-term sustainability.
V. What is Included in a TEV Study?
A Techno-Economic Viability (TEV) study is a comprehensive report that evaluates every critical dimension of a project. The aim is to assess whether the project is worth pursuing—technically, economically, and financially.
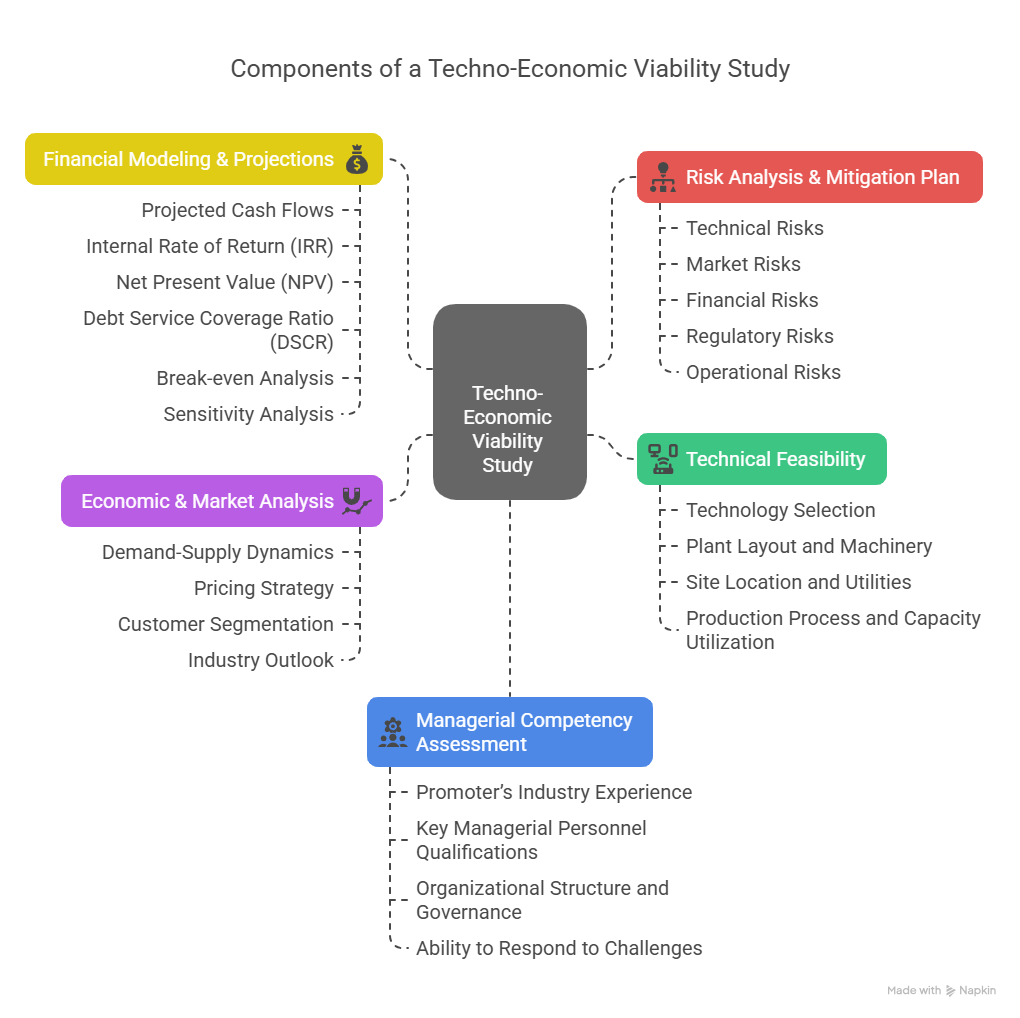
1. Technical Feasibility
This section of the study evaluates:
- Technology selection: Is the chosen technology proven, scalable, and up-to-date?
- Plant layout and machinery: Are the specifications and sourcing aligned with industry standards?
- Site location and utilities: Availability of raw materials, electricity, water, manpower, logistics, etc.
- Production process and capacity utilization: Can the project operate efficiently under the projected load?
The consultant reviews design documents, vendor quotations, and site plans to form a detailed technical opinion.
2. Economic & Market Analysis
Here, the consultant analyzes:
- Demand-supply dynamics in the target market
- Pricing strategy and cost competitiveness
- Customer segmentation and market positioning
- Industry outlook, government policies, and emerging trends
This section is particularly vital in sectors like manufacturing, renewable energy, and agro-processing, where market assumptions can make or break the project.
3. Financial Modeling & Projections
A well-structured TEV report includes a detailed financial model, often covering a 7–10 year horizon. Key components are:
- Projected cash flows
- Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
- Net Present Value (NPV)
- Debt Service Coverage Ratio (DSCR)
- Break-even analysis
- Sensitivity analysis
The objective is to evaluate the profitability, liquidity, and financial sustainability of the project under different scenarios.
4. Managerial Competency Assessment
Banks and investors place significant emphasis on the execution capability of the promoter and the management team. The TEV consultant assesses:
- Promoter’s industry experience
- Key managerial personnel qualifications
- Organisational structure and governance
- Ability to respond to challenges and scale operations
Strong leadership is often the differentiating factor in successful project implementation.
5. Risk Analysis & Mitigation Plan
Finally, the report identifies potential risks and proposes mitigation strategies. This includes:
- Technical risks: Technology failure, process issues
- Market risks: Demand uncertainty, pricing volatility
- Financial risks: Cost overruns, funding gaps
- Regulatory risks: Environmental clearances, legal compliance
- Operational risks: Delays, skill shortages
The goal is to give stakeholders a realistic risk-reward profile of the project.
VI. The TEV Study Process in India
A Techno-Economic Viability study follows a systematic, structured approach. Each phase is designed to collect and validate data, ensuring that financial institutions and stakeholders get a comprehensive, unbiased evaluation of the project.
1. Initial Client Engagement
The process begins with a preliminary discussion between the TEV consultant and the project promoter. Key elements covered at this stage include:
- Project overview and objectives
- Sector and industry of operation
- Funding requirements and timelines
- Documentation readiness
This helps the consultant assess the complexity of the assignment and prepare a proposal for scope, timeline, and fees.
2. Data Collection & Site Visit
Once the engagement is confirmed, the consultant requests:
- Detailed Project Report (DPR) or Feasibility Report
- Cost estimates and quotations for machinery
- Market research, licenses, and approvals
- Financial statements of the promoter
- Organizational structure and key personnel details
A site visit is often mandatory, especially for greenfield or expansion projects. The consultant evaluates the physical infrastructure, land, connectivity, and proposed setup.
3. Technical Evaluation
The engineering team assesses:
- Appropriateness of selected technology
- Machinery specifications and capacity
- Utility requirements vs. availability
- Implementation schedule and timelines
If required, the consultant may also interact with vendors, EPC contractors, and consultants involved in the project to confirm technical assumptions.
4. Economic & Market Feasibility
The financial team conducts in-depth market research using:
- Industry reports
- Government policies
- Competitive benchmarking
- Pricing forecasts
This section determines the commercial potential of the project under various demand scenarios.
5. Financial Analysis & Modeling
A core part of the TEV process, this step includes:
- Project cost break-up
- Assumptions on revenue, costs, and margins
- Loan structure and funding mix
- Financial projections (P&L, Balance Sheet, Cash Flow)
- Computation of IRR, DSCR, NPV, and Break-even
- Sensitivity and scenario analysis
This is presented in a bank-ready format to help in credit appraisal.
6. Risk Identification & Mitigation
At this stage, the consultant highlights:
- Project-specific and sector-specific risks
- Legal, environmental, or regulatory concerns
- Gaps in project planning or execution
- Mitigation strategies and contingency measures
This helps lenders and investors understand potential pitfalls.
7. Final Report Submission
The final TEV report is submitted in both hard and soft formats. It includes:
- Executive summary
- Detailed technical and economic assessment
- Financial model
- Observations, concerns, and recommendations
Some banks may ask for revisions or clarifications before final acceptance.
VII. Key Sectors that Require TEV Studies
TEV studies are most prevalent in sectors that involve high capital investment, long gestation periods, and significant technical inputs. Here are some major sectors in India where TEV consultants are routinely engaged:
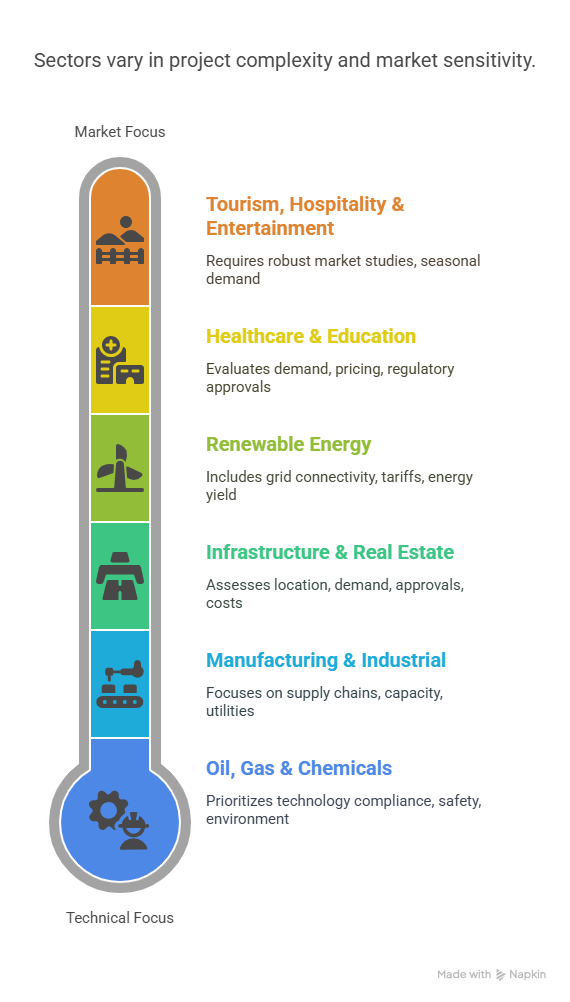
1. Manufacturing & Industrial Projects
- Steel, cement, textiles, plastics
- Electronics, auto components, heavy engineering
- Food processing and agro-based industries
These projects require careful evaluation of supply chains, plant capacity, and utility requirements.
2. Infrastructure & Real Estate
- Roads, highways, bridges
- Warehousing, logistics parks
- Townships, industrial estates
Here, TEV studies assess feasibility based on location, demand forecasts, approvals, and project costs.
3. Renewable Energy
- Solar and wind power plants
- Biomass and waste-to-energy projects
- Hydroelectric and hybrid models
TEV reports for this sector must include grid connectivity, tariffs, energy yield calculations, and environmental factors.
4. Healthcare & Education
- Hospitals, diagnostics centres, pharma manufacturing
- Universities, schools, skill development centres
Consultants evaluate demand, pricing, regulatory approvals, and operational viability.
5. Tourism, Hospitality & Entertainment
- Hotels, resorts, and convention centres
- Theme parks, multiplexes, water parks
These projects involve seasonal demand variations and require robust market studies.
6. Oil, Gas & Chemicals
- Refineries, petrochemical units, chemical plants
- LPG bottling, ethanol manufacturing
Here, the emphasis is on technology compliance, safety, and environmental clearances.
VIII. Difference Between TEV Report and DPR
Although often confused, the TEV Report and Detailed Project Report (DPR) serve distinct purposes in the lifecycle of a project. Both are important, but their use cases and target audiences vary significantly.
Aspect | DPR (Detailed Project Report) | TEV Report (Techno-Economic Viability) |
Prepared by | Typically prepared by the project promoter or a third-party technical consultant | Prepared by an independent, neutral TEV consultant |
Purpose | To showcase the project in detail and convince potential investors or lenders | To verify and validate the technical and economic feasibility for lenders |
Perspective | Promotional and project-positive | Analytical, critical, and risk-oriented |
Includes | Technical plans, project cost, market analysis, and implementation schedule | Independent analysis of the DPR, financial model validation, and risk identification |
End Users | Investors, partners, management | Banks, NBFCs, and FIs for credit appraisal |
Regulatory Requirement | Not mandatory | Often mandatory for large loans or stressed asset restructuring |
A good TEV consultant cross-examines the DPR in detail, challenges assumptions, validates costs and timelines, and evaluates overall sustainability.
X. Conclusion: Why TEV Consultants Are Strategic Enablers
In India’s evolving economic landscape, especially with the surge in infrastructure projects, renewable energy, and manufacturing, the role of TEV consultants has become indispensable.
Lenders face increasing pressure to reduce NPAs and ensure that their credit decisions are based on sound, independent analysis. Promoters need their projects evaluated objectively to instill lender confidence. TEV consultants sit at this critical intersection.
They not only enhance the quality of financial decisions but also minimize risk and increase project viability in the long run.
Whether you are:
- A startup planning a capital-intensive project,
- A seasoned promoter seeking expansion funding, or
- A lender evaluating a high-ticket loan proposal—
A professionally executed TEV study can make or break the decision.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A TEV (Techno-Economic Viability) report evaluates a project's technical feasibility and financial viability. It is crucial for securing loans or investments in India, especially for large-scale infrastructure, manufacturing, or renewable energy projects.
Banks, NBFCs, and financial institutions require TEV studies for loan appraisal, particularly for term loans above ₹10–25 crore. Project promoters, investors, and private equity firms also use TEV reports for due diligence.
While a DPR is created by the promoter to present project details positively, a TEV report is an independent, third-party evaluation that critically examines the DPR’s assumptions and validates feasibility for lenders.
Sectors like infrastructure, manufacturing, renewable energy, real estate, healthcare, and agro-processing frequently engage TEV consultants due to high capital needs and regulatory scrutiny.
TEV report preparation typically takes 2–4 weeks, depending on project complexity. Costs range from ₹50,000 to ₹5 lakh, based on the consultant’s profile and scope of work.


